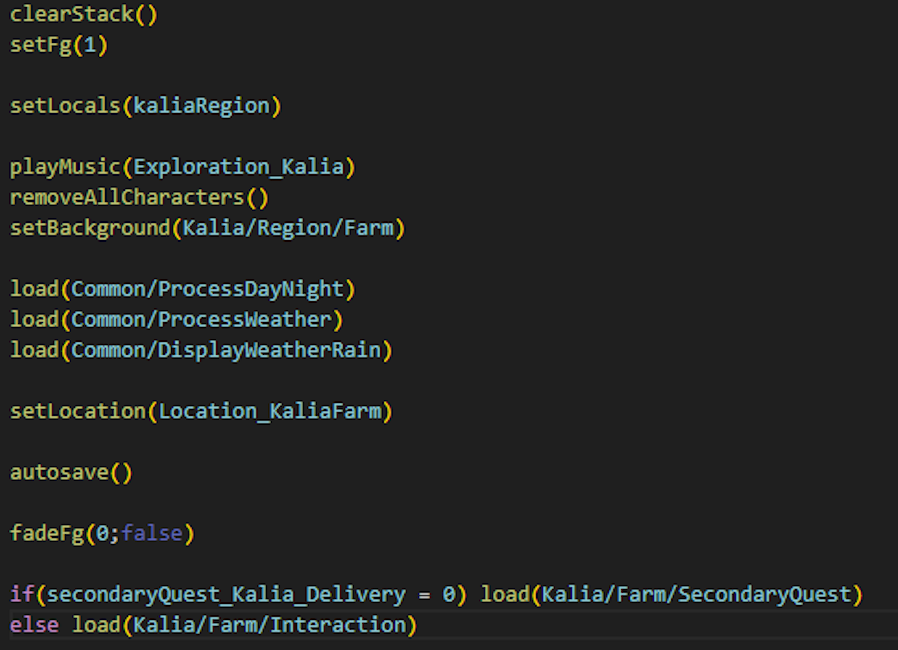
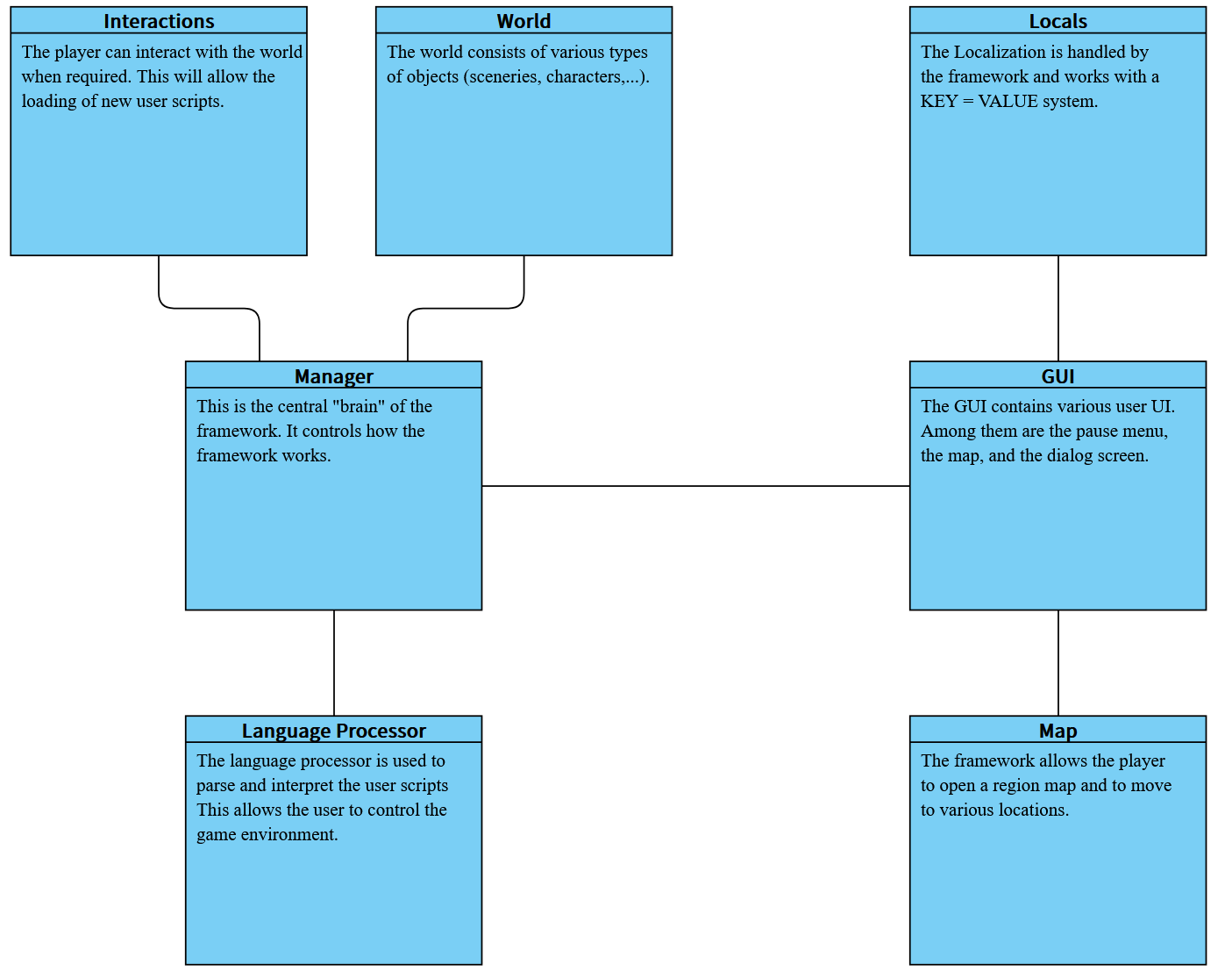
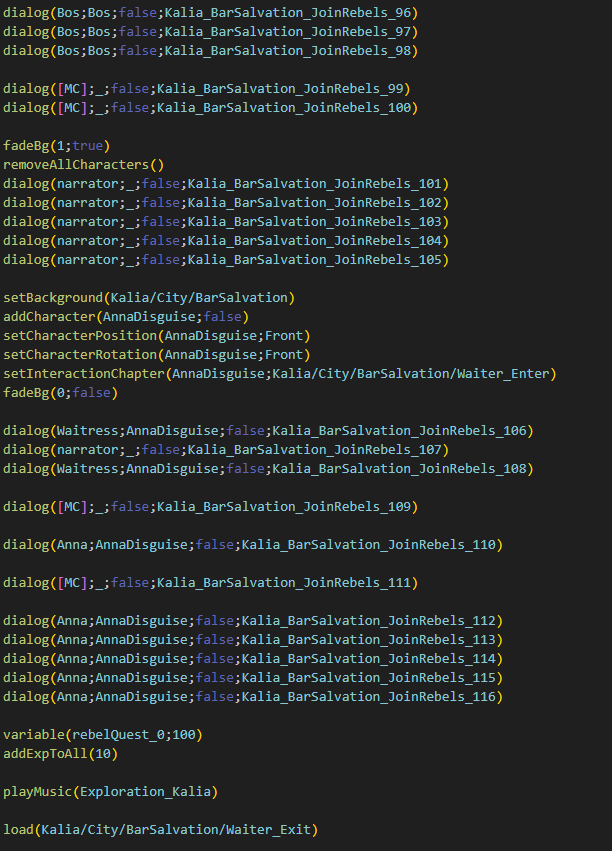
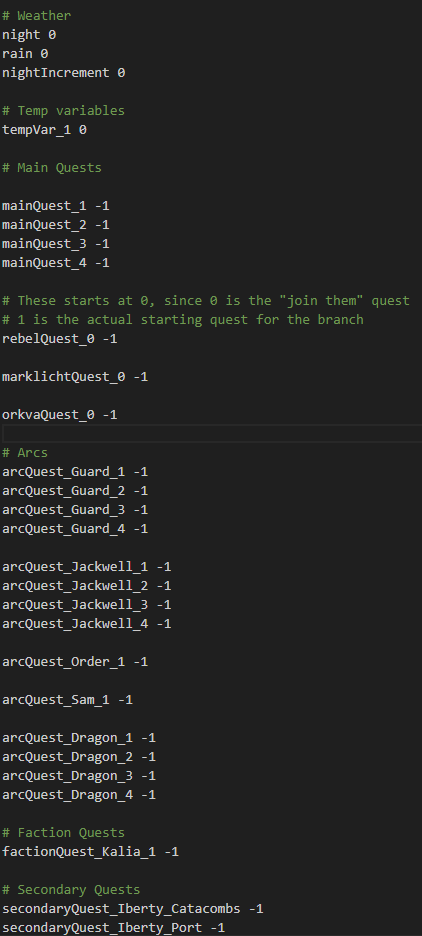
Framework history
ANF is a framework initially used to create 2D Visual Novels. It evolved over time and is now a framework focused on the creation of 3D non-linear point & click / visual novel.
As a result, it had during the past few years different forms, and even names. You can distinguish 4 phases in its evolution:
- The pre-framwork phase was the first phase of the framework.
It includes the first Harold's Quest games made at the time in Python and Javascript.
Initially, it consisted simply of functions allowing the display of dialogues and the activation of events.
It was still necessary to code the game in python, even if the functions made the work easier.
The first real version of the framework was created with Harold's Quest 2. The game used a handmade game engine and allowed its user to create a visual novel almost without having to touch python code.
Although this version was functional, it had some flaws (poor memory management, internal representation of dialogues not effective enough, ...) which did not make it viable in the long term.
- The early framework phase was the second phase of the framework.
It includes some Harold's Quest games, but also other games that have nothing to do with the series.
The latter generally reuse the framework's localization system, as well as the script processor.
This phase marks the beginning of the framework on Unity, with a drastic change on its inner working.
The script processor was created to control more simply in-game events, and a first version of ANSL (Adventure Novel Scripting Language) was conceptualized.
- The modern framework phase was the third phase of the framework.
It includes the remakes of the Harold's Quest games, but also student projects.
The latter reuse the framework's localization system, as well as the script processor. The twist is that the systems used by these student projects have been modified.
The location system has been improved (performance and accessibility), and a nodal version of ANSL, more accessible for non-programmers, was created.
On the side of Harold's Quest games, this phase marks the transition to 3D point & click. ANSL, the script language of the framework has been reworked to be more accessible and simple to use.
The framework itself has been reworked to be more pleasant to look at and easier to modify afterwards.
In the case of the remake of "Le Joyau du Nord", an alternative version of the framework was created to support the different RPG mechanics of the game.
- The final phase of the framework will be the fourth phase of the framework.
It will represent the creation of a standalone version of the framework, using different parts from previous games.
The localization system will use the version of My Herbarium, and the rest will be inherited from the remake of "Le Joyau du Nord".
Stability changes will be made to the framework to make it more accessible to a larger audience, and accessibility features will be implemented.
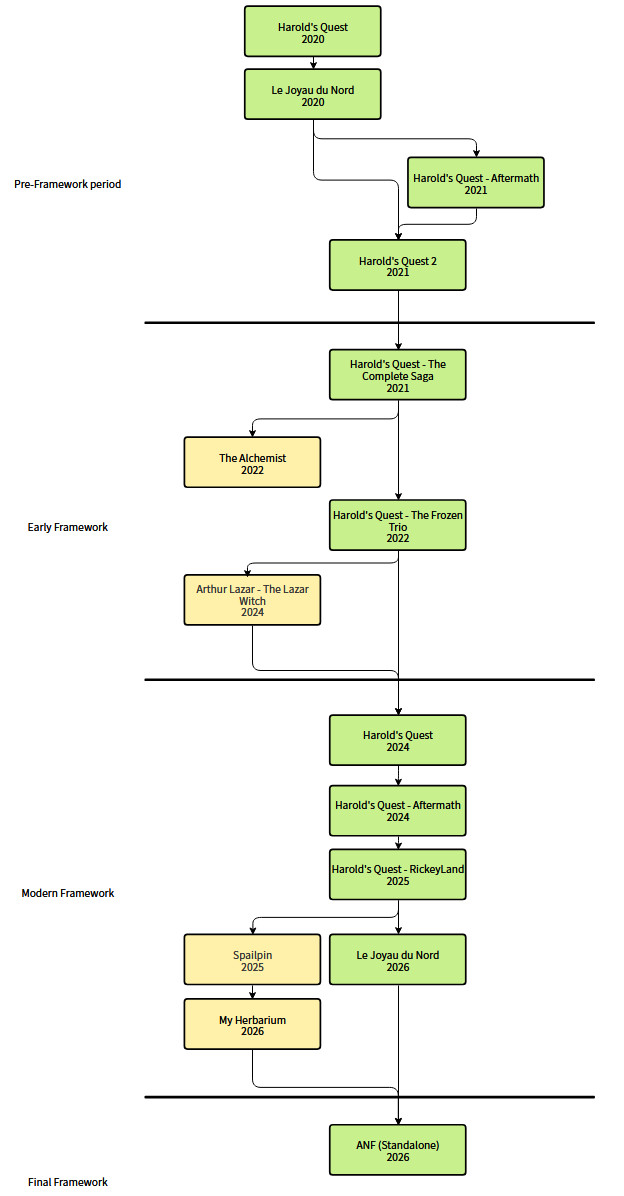
Diagram of the evolution of ANF. Games in green inherit the entirety of the framework. Games in yellow inherit only parts of it.